
Multiple new studies on human tissue and lab animals have provided the first insight into why the Omicron variant, though more contagious, causes milder disease than previous strains of Covid-19.
Research carried out on mice and hamsters by a team of Japanese and American scientists showed that Omicron, which first emerged in South Africa in November, produces less damaging infections, often limited to the nose, throat and windpipe.
The study also found the strain did much less harm to the lungs – whereas previous variants would often cause serious breathing difficulty and scarring – and that rodents infected with Omicron lost less weight and were less likely to die.
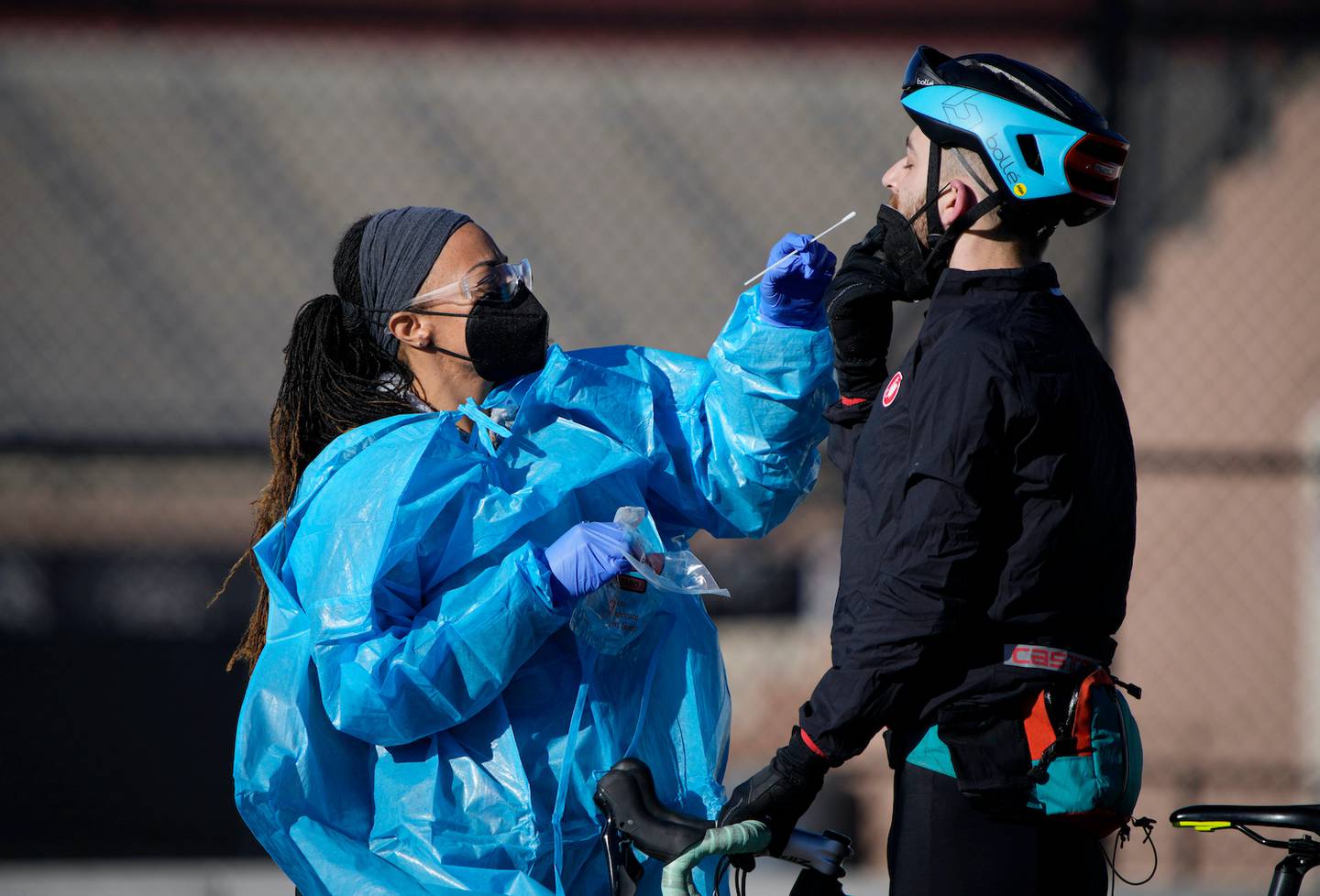

A medical technician performs a nasal swab test on a cyclist queued up in a line with motorists at a Covid-19 testing site near All City Stadium in Denver. Photo / AP
To the team's surprise, Syrian hamsters, a species known to get severely ill with all previous versions of the virus, also experienced much milder symptoms with Omicron.
"This was surprising, since every other variant has robustly infected these hamsters," Washington University virologist and co-author of the study, Dr Michael Diamond, told The New York Times.
A similar finding came from University of Hong Kong researchers, who studied bits of tissue taken from human airways during surgery.
The scientists found that Omicron grew more slowly than Delta and other variants did in 12 lung samples.
"It's fair to say that the idea of a disease that manifests itself primarily in the upper respiratory system is emerging," Berlin Institute computational biologist, Roland Eils, who has studied how coronaviruses infect the airway, told The Times.
The findings, which will have to be followed with further studies, such as examining the airways of people infected with Omicron, could explain why people infected with the variant seem less likely to be hospitalised than those with Delta.
Closer to home in NSW, while case numbers continue to soar, driven by the transmissibility of the variant, hospitalisation numbers have remained relatively steady, as has the number of patients admitted to intensive care as a result of the strain.
During the state's Delta outbreak in mid-2021, a quarter of hospitalised patients were in the ICU whereas, at the moment, it's less than one-in-10.
Children take advantage of empty shopping streets and galleries to play ball during a lockdown in Amsterdam, Netherlands, due to Omicron outbreak. Photo / AP
The number of ICU patients in NSW requiring a ventilator is also down. During the Delta outbreak, the percentage of people in intensive care who required ventilation was over 20 per cent; now, only 2 per cent of patients require the use of one.
"Hospitalisations are rising, but not at the same rate as newly reported cases, even allowing for a time lag, as people who go on to develop serious symptoms usually do so a week or more into their infection," chair of epidemiology at Deakin University, Catherine Bennett, told news.com.au on Friday.
Professor Bennett pointed to early studies published in both the UK and South Africa in December, which also suggest that people who contract the variant are far less likely to face severe illness and admission to hospital than those who contract the Delta variant.
Both countries have also reported "that Omicron infections that do lead to a hospital admission result in shorter stays on average, and this also helps keep numbers down on any given day, relative to other variants", she said.
While the studies clearly help explain why Omicron causes milder disease, they don't go far in helping scientists understand how the variant spreads so effectively from one person to another.
"These studies address the question about what may happen in the lungs but don't really address the question of transmissibility," University of Pennsylvania virologist, Sara Cherry, told The Times.
A separate study, published last week, reported that Omicron carries a mutation that may weaken innate immunity – a molecular alarm that activates our immune system at the first sign of an invasion in the nose.
"It could be as simple as, this is a lot more virus in people's saliva and nasal passages," Dr Cherry said, though she added the strain could also spread more efficiently because it's more stable in the air or better infects new hosts.
"I think it's really an important question."
Regardless, health experts around the world continue to stress that a lower chance of hospitalisation and severe disease if you contract Omicron shouldn't mean it's taken less seriously.
"It is probably not yet time to rest on our laurels," Dr Amir Khan wrote for Aljazeera earlier this week.
"Omicron cases have been rising across the world, far faster than initially thought. The United States and the United Kingdom are reporting record daily cases, with cities like London and New York worst affected.
"Even accounting for 40-50 per cent less severity and hospital admissions, if there are three times more cases, that will result in more hospitalisations and deaths than what we saw with Delta."
Dr Khan warned that the number of people forced to isolate – even without hospitalisation – "will inevitably start to affect front line services".
"The other danger is if the public holds onto this 'milder' narrative, there is a risk that some people may become complacent about regular lateral flow testing, mask-wearing and ventilating indoor spaces," he said.
"It may even lead to fewer people taking up the booster vaccines. This will then result in further cases and eventually an increase in hospitalisations and deaths."
- by Natalie Brown, news.com.au
Take your Radio, Podcasts and Music with you









